Wise Up
What Is The RBI? Functions & Objectives

Do you ever wonder what a classroom of 5-year-olds would look like without the supervision of teachers?
It would be mayhem if not complete anarchy!
Much like that room of over-excited children, the economy of India would be in complete disarray without the presence of a strong, fair, and efficient governing body. Which is why we’re lucky to have the Reserve Bank of India.
What is RBI?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is a regulatory institution in India that is tasked with safeguarding monetary stability in the country. Officially, this is The Preamble of the RBI (Source: RBI), which describes its basic function as such –
“to regulate the issue of Bank notes and keeping of reserves with a view to securing monetary stability in India and generally to operate the currency and credit system of the country to its advantage; to have a modern monetary policy framework to meet the challenge of an increasingly complex economy, to maintain price stability while keeping in mind the objective of growth.”
The RBI is critical to the economic development of our country, and to methodically implement this goal, it has laid out certain functions, each to enact a particular goal.
Functions & Objectives of the RBI
Functions of the RBI
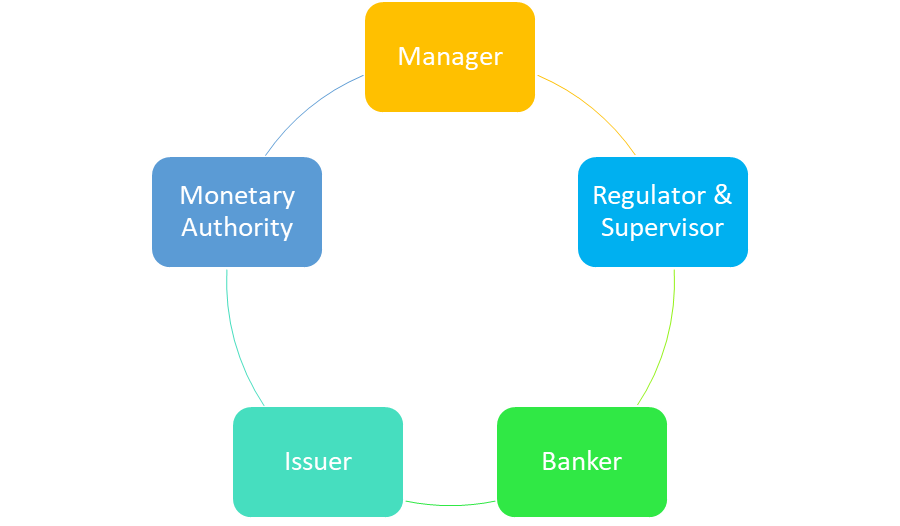
There are 5 key functions of the RBI, along with key objectives of their focus. These include –
- Monetary Authority – The RBI is responsible for formulating, implementing, and monitoring the monetary policy in India. So, these three functions that fall under the purview of the RBI address all the important policies that the government has mandated citizens and institutions follow.
OBJECTIVE – Being the monetary authority allows the RBI to maintain the stability of prices while also ensuring that the economy is growing. You see, this objective of the RBI helps the economy meet its own objective – to keep on flourishing! For the economy to grow, it is important that one single authority is there to oversee things and make sure everything is functioning smoothly.
2. Regulator & Supervisor – You see now why we went with the teacher analogy, right? The RBI is tasked with prescribing parameters for any financial systems in the country. So banking operations, savings schemes, and of course, investing – every facet of the financial system in India is regulated and supervised by the RBI.
OBJECTIVE: Having a regulatory institution in place instills public confidence. You know you sigh a sigh of relief when you see something is regulated or validated by institutions like RBI or SEBI! This is because the RBI ensures that you always have access to cost-effective financial services (be it banking, investing, or trading) and that your interests are always safeguarded. (Thank you, RBI!)
3. Manager – The RBI is the sole manager of foreign exchange in India. Under the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999, the RBI was granted certain special permissions that tasked it with being in charge of all foreign exchange activities in the country. So, when you come back from a family visit with some foreign currency and get it converted to Indian currency – the RBI is making sure that the process of this conversion is carried out to the tee.
OBJECTIVE: Foreign exchange is extremely important to the economy of any country. The RBI ensures that all external trade (whether for services, commodities, or currency) is carried out systematically and safely. The RBI aims to promote the proper development of and maintenance of any and every aspect of the foreign exchange market in India.
4. Issuer – The RBI is responsible for issuing, exchanging, and destroying (when needed!) currency notes, and for the circulation of all coin currency minted by the Government of India. Any currency you’ve got in your wallet – it’s all circulated through this single institution. (Shoutout to the OG ‘issuers of currency’ in all our lives – Mom & Dad!)
OBJECTIVE: At any given time, there needs to be enough currency notes and coins – in usable and undamaged quality – for the citizens of our country to use. The sudden deficit in physical currency can be quite catastrophic. The RBI ensures that currency is routinely circulated, exchanged, or even eliminated.
5. Banker – The RBI is a banker to the Government of India. According to the RBI website, it “performs merchant banking functions for the central and state governments”. This means that any payments or receipts that are made to the Government, are handled by the RBI. It carries out the exchange and remittance of funds, as well as public debt for the Indian government.
OBJECTIVE: It’s the boss bank, guys! That’s the easiest way to say it. The RBI is entrusted with being the bank for the Government of India, and as such it performs most of the functions that a regular bank would perform for you. (Another shoutout to the OG ‘banks’ in all our lives – Mom & Dad!)
Ultimately the RBI’s objectives (and by proxy, its functions!) have to be aligned with the national developmental goals of our country, to make sure the economy is growing as per the central government’s directive.
- More From The Finance

